


Thanks for registering
We encountered a previous register of this Medical ID. An email has been sent for instructions to activate this account.

Welcome to Abbott platform


A code was sent to you via email, please insert the verification number



En nuestra base de datos encontramos un registro previo.
Se ha enviado a tu correo electrónico un email para activar tu cuenta.


No se pudo validar su cuenta.
test.
Biologics for HCPs
January 7, 2026

It is estimated that biosimilars will generate savings of up to $290 billion globally by 2027, freeing up healthcare systems to support more people.1 They are also improving affordability.2 For instance, where an originator biologic medicine can require an $800 million investment and 8–10 years of development, biosimilars can markedly reduce this investment by as much as eightfold.2 These scientifically developed alternatives to originator biologics can offer substantial cost savings that could be reinvested into healthcare systems, unlocking broader access to life-changing therapies.
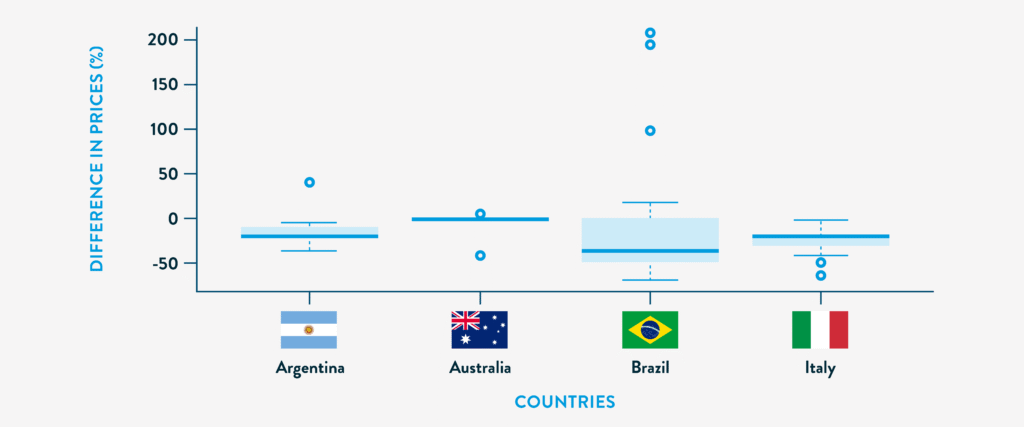
In a cross-national study of biosimilar pricing across Argentina, Brazil, Italy, and Australia; Brazil showed the highest median price reduction at 36.3%, with nearly half of its biosimilars priced over 40% below the originator.3
With biosimilars, physicians have more treatment options to suit diverse patient needs, while patients – especially those in resources constrained environments – can gain greater access to biologic medicines. This is especially important in middle to low-income countries, where high costs have traditionally limited the use of biologics.4 Biosimilars can help close this gap, facilitating more equitable healthcare delivery on a global scale.

However, the global picture is still uneven. In some countries, biosimilar regulatory guidelines have yet to be established, or their status remains unknown, which could slow patient access.5 Addressing these gaps is essential to ensuring that the benefits of biosimilars reach patients everywhere, not just in markets with established frameworks.

In 2021, biologics made up nearly half of all U.S. prescription medicine spending, totalling $256 billion, despite representing only around 3% of prescriptions.6 In 2024, the European Union spent €95 billion on biologics, accounting for 41% of its pharmaceutical expenditures.7 This level of spending is not sustainable for patients or health systems.
Biosimilars play a critical role in addressing this imbalance. By fostering constructive market competition, they help lower costs and expand access to life-changing treatments.7 In fact, as of July 2024, the cumulative savings at list prices from the impact of biosimilar competition in Europe reached €56 billion.7
As more biosimilars reach the market (with 40 FDA-approved and over 100 in development*) they offer a scalable solution to rising healthcare costs. When biosimilars are adopted, both biosimilars and their reference biologics become more affordable, freeing up resources that can be reinvested in other areas of care.8
REFERENCE
As of 2023.
GLO-25-1335